Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan
A National Movement Towards a Drug-Free India
Summary
|
Drug addiction is a significant and growing concern across India, posing serious challenges to individuals, families, and society at large. It particularly affects the younger generation, leading to severe consequences, including rising crime rates, strained interpersonal relationships, limited economic prospects, and a broader detrimental impact on societal well-being. Substance use disorders constitute a major public health issue, intertwined with psychological distress, prejudice, stigmatisation, and community instability. Additionally, factors such as genetic susceptibility, mental health conditions, and dysfunctional family environments, including child abuse or neglect, significantly increase the vulnerability of individuals to substance abuse.
Article 47 of the Constitution of India, under the Directive Principles of State Policy, places a moral obligation on the State to curb the consumption of intoxicating substances that are injurious to health. In alignment with this constitutional mandate, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment launched the National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) in 2018, with a roadmap extending till 2025. The NAPDDR aims to address the growing challenge of substance abuse through a comprehensive framework focused on preventive education, awareness generation, counselling, treatment, and rehabilitation.
Assessing the Challenge: Key Findings from the National Survey (2018)
To accurately gauge the extent of this crisis, the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, in collaboration with the National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre (NDDTC) at AIIMS, New Delhi, conducted India’s first-ever comprehensive survey on substance abuse in 2018. The findings, published in 2019, provided crucial insights into the magnitude of drug dependency across the country:
Alcohol emerged as the most widely consumed psychoactive substance, with approximately 16 crore individuals using it. Of these, more than 5.7 crore people are severely affected, requiring immediate treatment and support for harmful or dependent alcohol use. |
Cannabis ranked second, with around 3.1 crore individuals consuming cannabis products, of whom approximately 25 lakh suffer from severe dependency. |
Opioids, one of the most harmful categories of drugs, are used by approximately 2.26 crore individuals, with nearly 77 lakh requiring urgent intervention and support. |
An alarming 8.5 lakh people are estimated to inject drugs intravenously, primarily concentrated in states such as Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Delhi, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana. |
An alarming trend is the high prevalence of inhalant usage among children and adolescents, significantly exceeding adult consumption. |
Substance abuse disproportionately affects males, who significantly outnumber females across all substances studied. |
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan

Recognising the critical challenge of substance abuse, the Government of India launched the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA) on 15 August 2020, a key initiative under the National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR). Initially implemented in 272 high-risk districts—identified through the National Survey on Substance Use and inputs from the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB)—the Abhiyaan has since expanded to encompass all districts nationwide. Envisioned as a transformative nation-building mission, NMBA aims to foster a healthy, disciplined, and drug-free youth population, thereby contributing to the broader goal of national development and social well-being.
Milestones of the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA) as of 4th May 2025

Objectives
|
|
|
Stakeholders & Target Groups

Key Components & Strategies
NMBA employs a three-pronged strategy:
- Supply Control: Managed by the Narcotics Control Bureau.
- Demand Reduction & Awareness: Led by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment through extensive outreach and awareness activities.
- Treatment & Rehabilitation: Provided by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
District Level Nasha Mukt Committees, headed by District Collectors/Magistrates, develop and implement localised action plans focusing on:
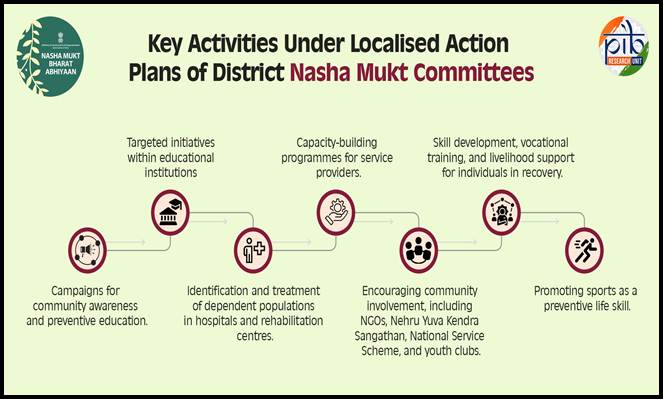
The ministry supports organisations that work for preventive education & awareness generation on substance abuse, capacity building, treatment and rehabilitation. These organizations are:
|
Technological Innovations
- NMBA Website: Offers comprehensive resources, real-time dashboards, e-pledge options, and expert-led discussion forums
- NMBA Mobile App: Collects and monitors ground-level data, with wide usage by Master Volunteers.
- National Toll-free Helpline (14446): Provides primary counselling and immediate referral services.
Conclusion
The Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan has evolved into a powerful nationwide movement, effectively mobilising communities and engaging diverse stakeholders in a unified effort to tackle the menace of substance abuse. Through targeted interventions, extensive awareness campaigns, innovative technological tools, and robust grassroots participation, the Abhiyaan fosters positive behavioural changes and empowers individuals and communities. As the campaign continues to expand and strengthen its impact, India moves closer to realising its vision of a healthier, resilient, and drug-free future for all its citizens.




addComments
Post a Comment